Representing algorithms for GCSE Computer Science
There are several ways to represent algorithms for GCSE Computer Science:
- Structured English
- Flowchart
- Pseudocode
- Program statements in a particular language
In this article we are looking at flowcharts for GCSE Computer Science.
For our example, we will create an algorithm which determines whether a given whole number is even or odd. The algorithm makes use of the MOD operator, which is represented in Python using the % sign. The principle is simple, but it can take some practice to get used to. MOD gives the remainder when dividing one integer by another. So for example:
- 5 divided by 2 gives 2 remainder 1
- 6 divided by 2 gives 3 remainder 0
Try running the Python code below to see how this pattern works when dividing by 2 and keeping the remainder.
for i in range(11):
print(i % 2)
Output:
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
Modulo operator lesson
If you want to master the modulo operator, check out this complete lesson with worksheets and practice examples, including Python code solutions. [product id=4961]
Flowchart the Even/Odd Algorithm
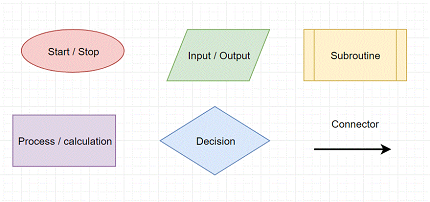
The flowchart for this algorithms is shown below. Make sure you can follow it, understanding all the symbols used. There is a key for the symbols at the top of this article.
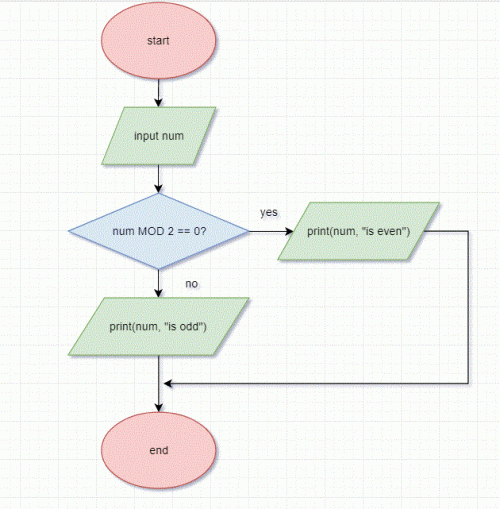
You should copy this flowchart on paper now to help remember and understand it. I recommend practicing flowcharts with paper and pencil as well as using an online tool such as draw.io
Programming the Even/Odd Algorithm in Python
Have a go now at writing the Python code for this algorithm. The solution is available by clicking on “show solution” but have a good attempt for yourself first.
Flowchart practice exercise
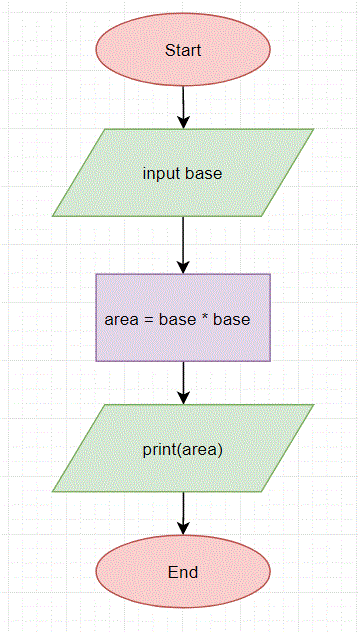
Draw a flowchart for an algorithm which takes the base length of a square as input and prints the area of the square.
Good luck with mastering flowcharts for GCSE Computer Science.